Beyond the Breach: Lessons Learned from 2024 Cyberattacks
In 2024, cyberattacks have shaken the digital landscape, exposing vulnerabilities and causing widespread data breaches. These events have reshaped cybersecurity practices, forcing organizations to reevaluate their cyber risk management strategies and invest in robust cyber insurance policies.
Incident Response: Lessons from Major Breaches
There has been a notable increase in cyber assaults in 2024, which have revealed weaknesses and resulted in extensive data breaches in numerous industries.
Cyber assaults are typically documented and scrutinized over time, and the complete ramifications of certain incidents may not be immediately apparent. However, considering patterns and documented incidents, it is reasonable to anticipate that various forms of attacks will likely be widespread in 2024.
Ransomware
Cybercriminals specializing in ransomware often direct their attacks toward critical infrastructure, healthcare institutions, and businesses, intending to extort financial benefits.
Regrettably, as outlined in the Gen Q2/2024 Threat Report, the menace posed by ransomware shows no signs of diminishing; on the contrary, it is escalating.
Examples of ransomware from 2024
London Drugs, a retail company, recently faced a cyberattack in April 2024, during which hackers stole files from its corporate headquarters. According to the Financial Post, London Drugs was targeted with a ransom demand of $25 million, and a deadline for payment was set for Thursday, May 2nd. In response to the breach, the company refused to pay the ransom demanded by the cybercriminals.
However, since the attack, the hackers have released some of the stolen data. London Drugs expressed deep concern over this distressing situation and acknowledged that the compromised files may contain employee information.
This revelation came after Brett Callow, a threat analyst with Emsisoft, an anti-virus software company, posted on social media that the hacking group known as LockBit claimed responsibility for the attack and released what it claimed was the London Drug’s company data. The attack resulted in the closure of all 79 London Drugs stores for over a week.
Data Breaches
Data breaches remain a lucrative target for cybercriminals, who seek to obtain sensitive personal and corporate information. Such breaches have severe consequences, including identity theft, financial fraud, and damage to reputation. Data that is highly sought after by fraudsters globally includes:
- Employee login credentials
- Customer credit card information
- Social Insurance Numbers
- Bank account numbers
Examples of data breaches from 2024
In 2024, there was a significant incident of data breach involving Patelco Credit Union. This particular breach occurred in June and resulted in unauthorized access to sensitive customer information. The compromised data included personal details such as names, addresses, Social Insurance numbers, and financial information.
The attackers responsible for this breach are believed to be connected to the BlackSuit ransomware group. They managed to gain entry into Patelco’s systems and encrypt the data.
The Patelco Credit Union recently disclosed in an updated public filing that the personal data of over one million individuals, including current and former members and employees, was compromised.
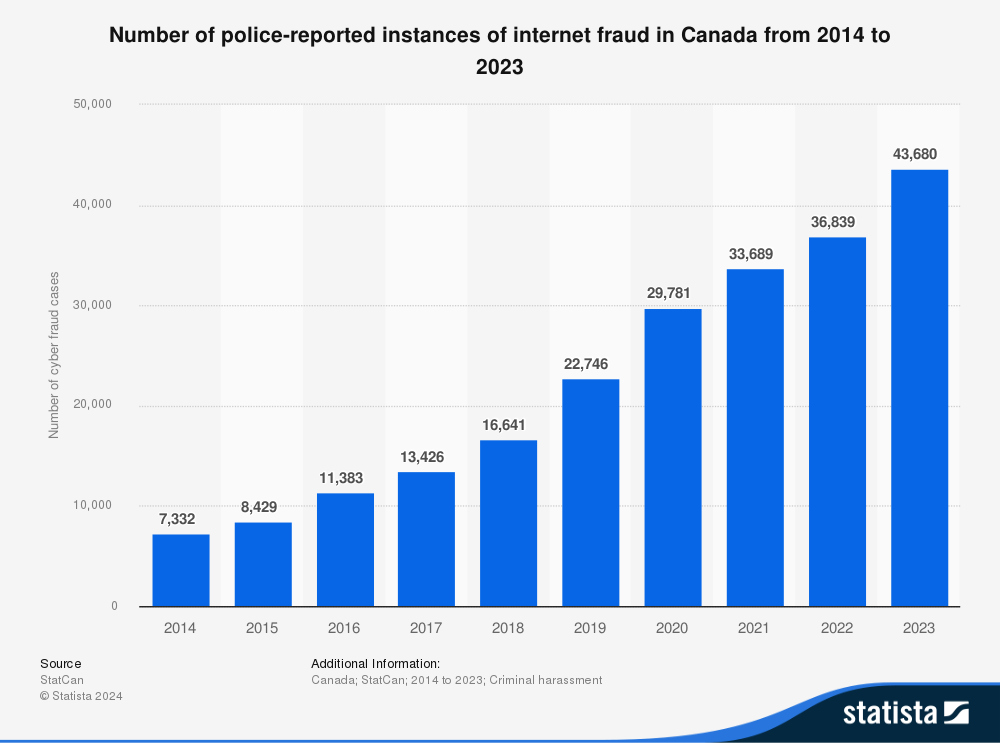
Details: Canada; StatCan; 2014 to 2023; Criminal harassment
Phishing and Social Engineering
These tactics involve deceiving individuals into clicking on harmful links or divulging personal information. These attacks can be utilized to distribute malware or obtain unauthorized entry into computer systems.
It is important to note that phishing attacks may even masquerade as communications from various types of organizations, including your own internal workplace or even non-profit charities. Attackers often take advantage of current events and certain times of the year, such as:
-
- Natural disasters (e.g., Hurricane Katrina, Indonesian tsunami)
- Epidemics and health scares (e.g., H1N1, COVID-19)
- Economic concerns (e.g., tax scams)
- Major political elections
- Holidays
Examples of data breaches from 2024
According to a recent survey conducted by Interac Corp., a payment processing company, government impersonation is a prevalent financial scam affecting individuals across Canada. The survey revealed that 42% of the respondents reported encountering scammers who pretended to be representatives of official government institutions.
Government Representative Scammers Statistics
Related to phishing scams
Related to fake banking, credit cards, and online accounts
Rachel Jolicoeur, the director of cyber market intelligence and financial crimes at Interac, emphasized the professionalism and opportunistic nature of these criminals:
There’s always a call to action and a sense of urgency…a
s soon as you get that feeling, just stop and pause on that to scrutinize.
The Interac survey, which collected responses from 1,202 individuals online between September 28th and October 6th. In recent months, the Canadian government has issued multiple alerts to caution citizens about the prevalence of fraudulent activities.
Interac Survey Respondent Feedback to being Targeted by Fincial Scams:
Is a common occurrence in Canada
Expressed worry about falling victim to scams
Data Breaches Report from 2024
Cost Per Data Breaches Paid by Canadian Organizations(by the million):
Average for Canadian Organization
Average for Financial Services Sector
Average for Technology Companies
Interestingly, the average cost of data breaches has decreased compared to the previous year. Additionally, Canada has dropped from the third position globally for the costliest data breaches to the sixth position.
This reduction in breach costs can be attributed in part to 61% of Canadian companies’ adoption of security AI and automation to prevent such incidents. According to a study conducted by IBM, companies that heavily incorporate Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation into their security operations experienced breach lifecycles that were 54 days shorter than those organizations that did not utilize these technologies.
Daina Proctor, IBM Canada’s security service line delivery leader, commented:
Canadian organizations that invest in AI and automation will be better equipped to detect and recover from breaches, reducing the significant costs associated with these events.”
“The findings of this report underscore the business imperative for companies to integrate AI and automation into their cybersecurity programs to reduce both the financial impact and business disruption of cyber breaches.
Evolution of Ransomware Tactics
Ransomware attacks have increased13% rise in ransomware attacks over the past five years, with an average cost of CA 2.57 million per incident in 2023.
The escalation in attack volume is evident, as organizations worldwide detected nearly half a billion ransomware attacks in 2022.
“The Gen Threat Report, formerly known as the Avast Threat Report, has revealed a 100% increase in ransomware activity for the US, UK, and Canada; 66% in Australia; and a whopping 379% in India.” – Nyrmah J. Reina
The severity of these attacks has also intensified. The average downtime a company experiences after a ransomware attack is now 24 days, causing significant disruptions to business operations. Moreover, the financial demands have reached unprecedented levels, with the highest ransomware payment demand ever recorded being CA 97.16 million.
Negotiation Strategies and Outcomes
As ransomware attacks have become more sophisticated, so too have the negotiation strategies employed by both attackers and victims. Cybercriminals have become more strategic in setting ransom expectations, often basing their demands on open-source information about the target organization’s revenue or cyber insurance coverage.
Ransomware negotiators play a crucial role in managing these high-stakes situations.
They engage with threat groups on behalf of the affected organization, attempting to lower ransom demands and buy time for the victim. However, some ransomware authors have threatened to delete decryption keys if professional negotiators intervene, adding another layer of complexity to the process.
Ransomware Outcomes Statistics:
Who submitted a ransom payment experienced another attack soon after
Regained access to their data, but most of it was corrupted
Emerging Threats: AI and Deepfakes
Growth of AI-assisted Attacks
The rapid adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) has introduced complex cybersecurity risks that traditional practices may not sufficiently address. From January to February 2023 alone, researchers observed a 135% increase in ‘novel social engineering attacks,’ corresponding to the widespread adoption of ChatGPT. This surge highlights the growing threat of AI-assisted cyberattacks.
One of the most significant concerns is using AI in social engineering attacks. Cybercriminals can now leverage AI language models to study a target’s entire email history and communication patterns, crafting perfectly authentic-sounding phishing messages. This capability allows them to build trust quickly and increase the likelihood of successful exploitation.
Can you spot the deepfake? How AI is threatening elections
Deepfake Risks for Businesses
Deepfakes – synthetic, AI-generated media designed to manipulate or replace existing video, image, or audio content with a fabricated version – pose a significant threat to businesses and individuals alike. These AI-generated fakes can have serious consequences, such as influencing political decisions or causing public panic.
Deepfakes can be used to undermine brand reputation, impersonate leaders and financial officers, and compromise vital data and systems. For example, a fake but realistic-looking video of a CEO making inappropriate comments or contradictory statements can severely damage a brand’s image and lead to significant reputation loss.
Key Lessons Learned
-
- ✓Implement Comprehensive Cyber Risk Management: Strategies must be holistic to address evolving threats introduced by new technologies like generative AI and third-party integrations.
-
- ✓Prioritize Rapid Detection and Response: Organizations that utilize AI and automation for security prevention saw a significant reduction in breach costs, saving an average CA $2.84 million compared to those that did not.
- ✓Maintain a Proactive Posture: Essential practices include regular cyber risk assessments, implementing advanced threat detection systems, and developing comprehensive incident response plans.
Stay Connected With Harvard Western
Thanks for reading our article; I hope you enjoyed this month’s topic on Cyber Attacks in Canada. Here are some more ways to access more insurance information and tips:
Visit our Blog/article page each month, where we publish various insurance articles and share information on specific industry products.
Learn more about or get a quote for Business Insurance, and visit our product page for comprehensive information.
Follow us on LinkedIn to stay up to date on the latest insurance articles and company updates.
Last updated:
Posted in Business on October 10, 2024 by Hope Prost